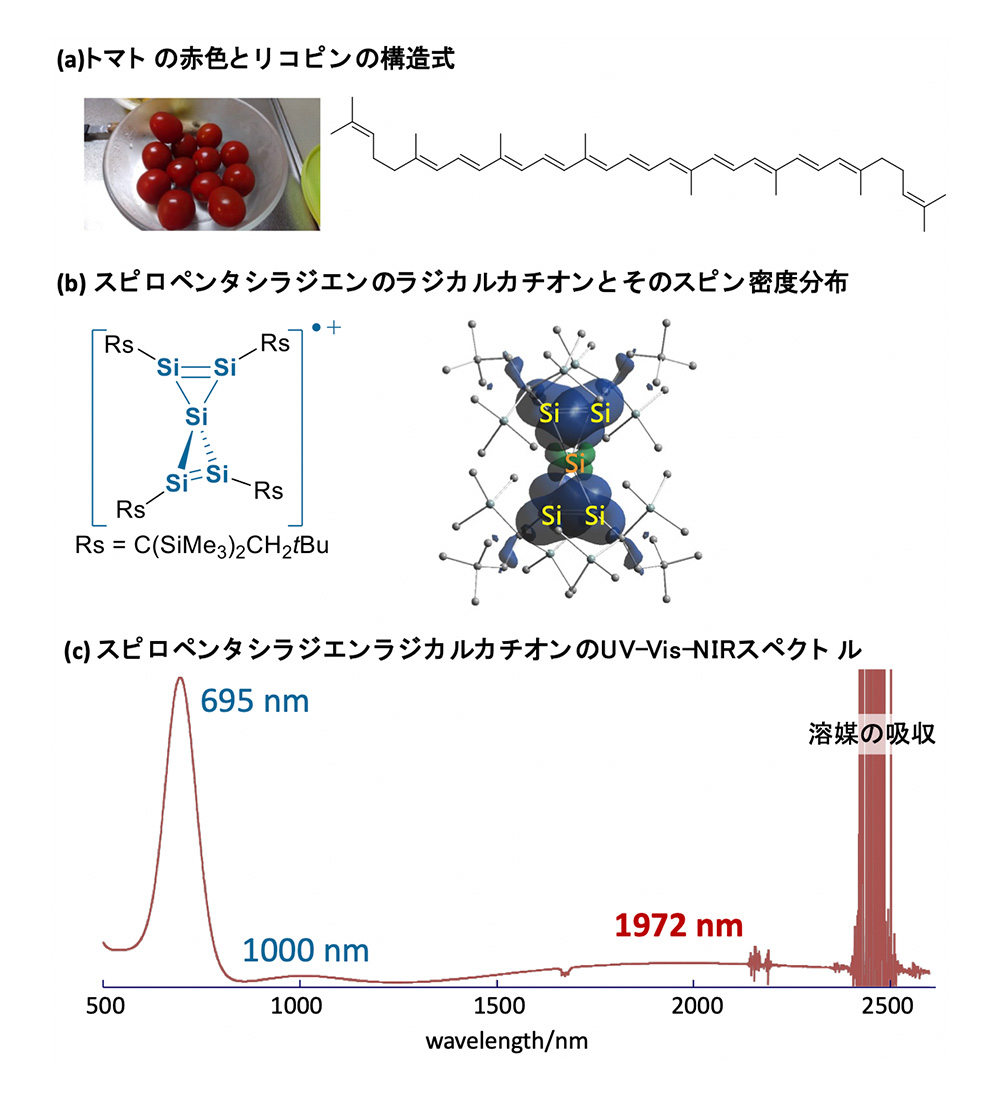
We isolated a spiropentasiladiene radical cation salt (Figure (b)) as a dark-green solid via the one-electron oxidation of a newly synthesized spiropentasiladiene. In this compound, the spin is delocalized across the perpendicularly located two Si=Si bonds. As shown in Figure (c), the longest-wavelength absorption band of 1 (λmax = 1972 nm) covers the IR-B region (1400-3000 nm; 0.89-0.41 eV) despite having the smallest possible spiroconjugation motif (five silicon atoms) in the UV-Vis-NIR spectrum. The unprecedented absorption band in the IR region was assignable to the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) → singly occupied molecular orbital (SOMO) transition that is resulted from the delocalized π-orbitals in the spirocyclic silicon skeleton.