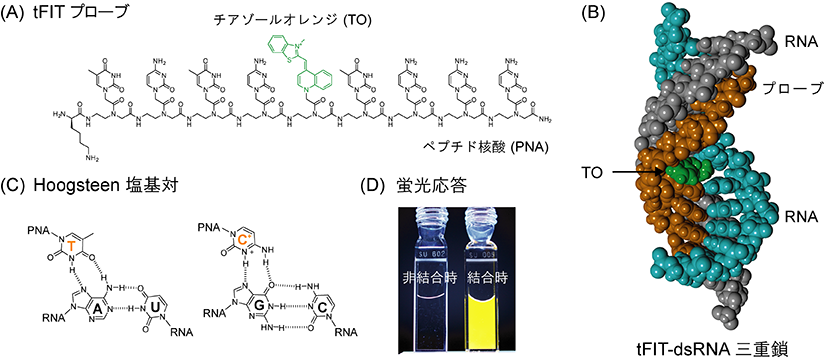
We have developed a new fluorescent sensing probe for double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) by integrating thiazole orange (TO) as a base surrogate into triplex-forming PNA. Our probe forms the thermally stable triplex with the target dsRNA at acidic pH; and the triplex formation is accompanied by the remarkable light-up response of the TO unit. The binding of our probe to the target dsRNA proceeds very rapidly, allowing real-time monitoring of the triplex formation. Importantly, we found the TO base surrogate in our probe functions as a universal base for the base pair opposite the TO unit in the triplex formation. Furthermore, the TO unit is significantly more responsive for the fully-matched dsRNA sequence compared to the mismatch-containing sequences, which enables the analysis of the target dsRNA sequence at the single-base pair resolution. The binding and sensing functions of our probe are described for the development of fluorescent probes applicable to sensing biologically relevant dsRNA.
Takaya Sato, Yusuke Sato, and Seiichi Nishizawa, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 9397-9400. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.6b05554